Hair
Restoration
We understand that addressing sexual health concerns can feel awkward or inconvenient. We're excited to offer a revolutionary approach!
Gone are the days of worrying about doctor visits, medications, or side effects. We're bringing state-of-the-art men's sexual health technology directly to you.

You have a question?

What’s Included in your Package
2. 5mL Exosome Vial to be added to the first PRP treatment
3. Theradome Helmet, to be worn 4x week for 10 minutes
4. Nutrafol for Men or Women x 4 months
5. 3 Peptides x 4 months:
- a. Hair Rescue: Repair Topical Solution
- b. Hair Rescue: Activate Topical Solution
- c. Thymosin Beta 4 (fragment) Oral Capsule
How Does Hair Grow?
Did you know that you produce ALL of your hair follicles during fetal development? There are approximately 5 million follicles located throughout the body with 1 million follicles on the head and 100,000 hair follicles on the scalp. You will not generate any additional hair follicles once you are born, this is all you get which is why we start to see the decline in hair follicles as we age and as our scalp expands. There are two distinct structures to this hair follicle; the follicle itself which is located below the skin and the shaft which is the visible part above the scalp.
1. Hair Follicle: A tunnel-like segment that extends from the scalp down into the dermal layer; I like to think about it as the roots to your tree. This segment contains several different layers with different functions and properties. At the base of the follicle is called the papilla, this is where your blood vessels and capillaries reside, or think about it as the soil that will be nourishing the roots to your tree. This is how you “feed” the cells surrounding the hair follicle, nourishing the tissue and keeping it healthy. This bottom portion of the hair follicle is also called the bulb and is considered the living part of the hair, it divides every 23 to 72 hours which is faster than any other cell division in your body. You have two protective layers to this hair follicle, the outer sheath and the inner sheath. The inner sheath extends all the way up to just below the sebaceous gland, the gland that is responsible for sebum or oil production which conditions the hair and skin. As we age, our sebum production begins to decline providing less and less oil to the hair follicle and scalp. The outer sheath continues all the way up to the sebaceous gland and up into the scalp protecting the follicle like a blanket.
2. Hair Shaft: This is what you see above the scalp and is the dead part of the tissue, or the actual tree trunk that you see in the backyard. It is made up of a hard protein called Keratin which is responsible for stimulating hair growth and is made up of three layers. The medulla is the inner layer, the cortex is the middle layer and makes up the majority of the hair shaft, and the cuticle is the outermost layer. Again, comparing this to the tree trunk and the rings inside if you were to cut the tree in half. The cuticle and the cortex are what is responsible for the pigment and color to your hair.

There are 3 Stages of Hair Growth
These 3 stages determine the length of the hair and each strand of hair is at its own stage of development. Once the cycle is complete, it restarts and a new strand of hair begins to form. Scalp hair grows at a different rate for each individual based on their genetics, environmental factors and their age. However, the average growth of a hair follicle is 0.6cm-3.36cm per month or 0.3mm a day.

1. Anagen: This is considered the active phase or growth phase of the hair. This stage begins in the papilla (the capillary and blood vessels section or the roots and soil) and can last anywhere from 3 to 5 years based on genetics. The longer the hair follicle stays in this stage, the longer the hair grows. People who have difficulty growing their hair tend to have shorter anagen phases. For example, the hair in your eyebrows, eyelashes, legs and arms have short anagen phases which is why they are much shorter than the hair on your head. It is during this phase that the follicle will bury itself into the dermal layer of the skin to nourish the strand, again similar to the roots and the soil of a tree. 85%-90% of the hairs on your head are in the anagen phase. This is an important stage that requires the maximum amount of blood flow and rich nutrients from the tissue to ensure hair growth. Again, if you think about this as a tree the soil must be rich in nutrients and have plenty of water to feed the roots.
2. Catagen: This phase is considered the transition phase and lasts about two to three weeks, approximately 3% of all hair follicles are in this stage. This is where the follicle renews itself, it detaches from the papilla cutting off the nourishment from the blood supply and begins to shrink due to its disintegration. This follicle is now called the “Club Hair”. This is when the hair follicle attaches itself to the hair shaft and a club hair develops. Club hair is the final product of hair growth and features a bulb of keratin at the root tip of the strand. The bulb is responsible for keeping the hair in the follicle until it is time for shedding. As the hair follicle produces new strands of hair, these new strands slowly replace and push out the club hairs.
3. Telogen: This is called the resting phase or shedding phase, a process that results in normal hair loss. The hair follicle remains dormant for one to four months and approximately 10-15% of hair is in this phase. The cells lining the follicle channel will continue to grow and accumulate around the base of the hair acting as an anchor and preserving the hair until the anchor allows the hair base to break free from the root and then the hair is shed. The new hair shaft will begin to emerge once the telogen phase is complete. About 25 to 100 telogen hairs are shed normally every day.
Are you the right candidate?
Why do you Lose Hair?
Multiple factors contribute to hair loss when the cycle of hair growth and shedding is disrupted or when the hair follicle is damaged. Those include; genetics, hormones, vitamin deficiencies, illnesses such as autoimmune disorders, and stress. The key to understanding and treating hair loss is to find and treat the root cause first rather than treat the symptoms. Let’s discuss this in detail.
1. Genetics “Androgenetic Alopecia”: The most common cause of hair loss is genetics, otherwise known as male pattern baldness and/or female pattern baldness. In men, it occurs gradually with aging and presents as an M-shaped receding hairline that starts in their 20s and 30s and progresses into bald spots. 80% of men will experience male pattern baldness by the age of 80. Women will start to experience thinning of their hair after menopause. It was commonly known that this genetic baldness would come from the mother’s side in the X chromosome, however in 2017 a new study revealed that there are over 63 genes responsible for genetic hair loss with only 6 of those genes coming from the X chromosome (mom’s side).
2. Hormones: Multiple hormones play a role in hair development such as the thyroid, testosterone, DHT, Estradiol, and Cortisol. An imbalance of any of these pathways can lead to the destruction of the hair follicle. For Thyroid, having too much or too little hormone (hyperthyroid or hypothyroid) can cause the hair to shed with thinning all over the head or hair loss on the side, hair can also become dry and brittle as it shortens the growth phase of the hair follicle. Too much Testosterone or the conversion of too much Testosterone into DHT (dihydrotestosterone), the active metabolite of Testosterone and more powerful androgen, binds to receptors in the hair follicles disrupting the cycle of hair growth leading to hair loss around the crown or forehead region. Elevated levels of Estradiol can increase your risk of insulin resistance, polycystic ovarian disease, and obesity and typically result in a low Progesterone level. Progesterone has been shown to inhibit the enzyme, 5-alpha-reductase, which converts Testosterone into DHT in the hair follicle. As previously mentioned, DHT disrupts the cycle of hair growth. High levels of cortisol, oftentimes due to excessive stress, reduce the production of certain elements needed for hair growth and increase the breakdown of hair-supportive elements by about 40%.
3. Vitamin Deficiency: Nutritional deficiencies in Iron, zinc, B vitamins, biotin, GLA and lack of protein (vegan diet) can also cause hair loss. Iron deficiency, along with thyroid disorders, are the two most common conditions associated with hair loss. A study showed that low levels of iron and L-lysine were the main cause behind excessive hair shedding otherwise known as telogen effluvium. A combination of zinc and biotin deficiency is associated with alopecia and total body hair loss as zinc is required for multiple hormone pathways. B12 is needed for the healthy production of red blood cells, which deliver oxygen and nutrients to the base of the hair follicle. GLA is an essential fatty acid that acts as an anti-inflammatory and improves hair texture and makes the hair follicle stronger. GLA is also known to be an inhibitor of the 5-alpha-reductase enzyme reducing the amount of Testosterone that is converted into DHT, preventing destruction of the hair follicle. Collagen is one of the best protein sources for hair health. As the body ages, the damaged DNA causes the collagen in the hair follicle stem cells to be broken down.
4. Medical Conditions/Illness/Autoimmune: Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disorder that allows the body to attack itself, thinking it is a foreign invader. This attack is specifically on the hair follicle itself, causing hair loss that occurs in round patches on the scalp. This condition is solely based on the immune system rather than the hair follicle. Heavy metal toxicity such as low stomach acid (perhaps you are taking an antacid or proton pump inhibitor), mercury tooth fillings, consuming too much tuna, or taking colchicine (a gout medication) can disturb the hair growth cycle. Chemical treatments or certain salon products or shampoos that contain sulfites can break down the disulphide bonds that hold together the chains of keratin that give hair flexibility and strength. If keratin gets broken down in the hair follicles, then hair loss will occur.
Two Drugs That Are FDA Approved For Hair Loss
1. Topical Minoxidil: This medication is now available over the counter in 2% and 5% solutions as well as 5% foam, otherwise known as Rogaine. It is approved for use in both men and women and is considered a vasodilator promoting increased blood flow to the hair follicle as well as prolonging the anagen phase of hair growth. There are side effects to taking this topical medication which include irritant or allergic contact dermatitis and increased facial hair in women.
2. Finasteride: This medication is a 5-alpha reductase inhibitor that is also known as Propecia and can be used for enlarged prostate or BPH. It prevents the conversion of Testosterone to its active form Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), thereby slowing the progression of hair loss and stimulating regrowth in patients with androgenetic alopecia. The use of finasteride is limited to men and, off-label, post-menopausal women as ingestion of finasteride in women of childbearing age can result in deleterious effects on a male fetus including ambiguous genitalia. Finasteride is also known for its sexual dysfunction side effects and has created what is now known as “Post Finasteride Syndrome”. A disorder that can cause persistent erectile dysfunction even after discontinuing the medication as well as depression, melancholy, and general loss of general well-being.
Important Note: Patients who choose to use either Minoxidil or Finasteride must be warned that discontinuation of either will result in regression and progression of alopecia, therefore continued use for hair loss is a must once started.

Works Cited Page
1. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Human_hair_growth
2. https://laylahair.com/what-is-club-hair-and-how-to-identify-it/
3. https://hormonesbalance.com/articles/causes-of-hair-loss-in-women-and-potential-treatments/
4. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4134641/
5. https://reactivehair.com/theradome-review/#:~:text=The%20Theradome%20helmet%20is%20a%20hair%20stimulating%20laser,
hair%20growth%20treatment%20for%20both%20women%20and%20men.
6. https://www.theradome.com/how-theradome-works
Frequent
Questions asked
What is PRP for Hair Restoration?
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a type of blood cell that makes your blood clot. It also plays a role in healing since it contains growth factors and cytokines, such as: Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), Transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-Beta), Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) just to name a few. These growth factors are essential for boosting the cell proliferation (cell growth) of the dermal papilla, differentiation (forming specialized cells such as skin cells), and chemotaxis (movement in response to chemical stimulus), increased permeability, reduce inflammation and prevent hair cell death (apoptosis). Ultimately, the growth factors in PRP also act on the stem cells that are found in the bulge area of the follicles. This results in neovascularization and folliculogenesis, which is extremely important for hair regeneration. In other words, PRP hair treatment prolongs the hair cycle or anagen phase, boosts hair regrowth, improves blood supply and reduces inflammation while also activating dormant hair follicles.
PRP has many other benefits which include: a down-regulation in autoimmune responses (by inhibiting inflammatory causing cells), an increase in fibroblast proliferation (wound healing), the creation of angiogenesis (new blood vessel formation) and collagen production, the ability to enlarge and multiply adipocytes (fat cells), to foster and create neurogenesis (new nerve cell formation) and it has shown to be beneficial in glandular function (secretion of hormones). Platelet-rich plasma has been shown to be effective in the treatment of joint pain, hair growth, skin rejuvenation, and sexual wellness.
PRP is taken from your own blood, drawn up into an FDA approved tube that includes a separation gel and an anticoagulant and then spun in a centrifuge which will then separate your platelet-rich plasma from your red and white blood cells. The PRP is then drawn up into several smaller syringes and injected into the scalp using a botox or insulin needle along the scalp line and into the sections of hair loss or thinning. One injection covers about 1 cm of hair, therefore several injections are needed to receive optimal results. The entire process takes approximately 30 minutes from start to finish and patients will begin to see improvements in as little as 4 weeks and up to 3 months. But the results don’t stop there, the tissue will continue to remodel and enhanced blood flow will nourish the follicle over the course of the year.
Why Do You Need 4 Treatments One Month Apart?
What is an Exosome and Why Add it to Your PRP?
Exosomes are nanosized “extracellular vesicles” that are one thousandth the size of a cell. They are produced by virtually every cell type as a means of intercellular communication. They are surrounded by a lipid membrane with proteins on their surfaces and are located within the Stem Cell itself. It is because of this lipid membrane that the Exosome material (proteins, mRNA and microRNA) is protected from degradation but also allows the exosomes to reach cells in parts of the body that medications are unable to. The proteins attached to the surface is what allows the exosome to reach their target cells, acting as the chemical messengers released by the Stem Cell to repair inflammation and damaged cells when called upon. Every Stem Cell in your body can secrete trillions of Exosomes naturally, so why not remove the “middle man”? Think of the Exosome as the “mailman” and the Stem Cell as the “post office”. All of the information or “mail/letters” must be housed at the Post Office for safe keeping, but when it is time to deliver the message to the correct recipient you need someone to deliver that message such as the “mailman” or the Exosome. What was once thought as the Stem Cell “sticking around” once injected to create new tissue and blood vessel formation was really just the Exosome, as most stem cells are cleared within a week of injection. The Exosome is also considered less risky than Stem Cells as they do not carry the DNA, genetic material, or the organelles and mitochondria from the host therefore they cannot replicate, they cannot transform into malignant cells or other harmful cell types, they are less likely to trigger an immunogenic response, and they cannot be infected with a virus. The lack of DNA is also what makes the rejection of these cells impossible and therefore lowers the risk of their use. They are much smaller than the Stem Cell, as nanosized particles are how they are categorized, and are thus able to cross the blood brain barrier as well as penetrate solid tissue masses such as the Thyroid gland or tumors, triggering the healing cascade. They are also simpler to harvest, store and transport making the cost more manageable for patients.
Exosomes from placental Mesenchymal Stem Cells, like the ones we use at Novus, have the potential to target every organ and tissue in the body, influencing your own dormant cells to come out of hibernation, proliferate and heal itself. They also have potent anti-inflammatory effects, changing macrophages and T-cells from inflammatory states to non-inflammatory states. They also seek out injured or damaged tissue and promote healing and homeostasis by their specific microRNA molecules that can help regenerate normal collagen in the skin and enhance extracellular matrix production to restore damaged tissue. They may even suppress tumor genes. They are considered pro-angiogenic, stimulating endothelial cell function, thereby improving angiogenesis. In other words, injecting placental MSC Exosomes into the scalp will provide the older, damaged hair follicles the necessary building blocks to become rejuvenated, healing the damaged tissue and weakened blood vessels as well as wake up dormant follicles. The results are much quicker when Exosomes are added to the PRP for hair restoration, the best way I like to think about it is this; how fast do you heal from an injury? How much do you grow each day? Now ask yourself the same question for babies. How fast do they heal from injury and how fast do they grow each day? These placental MSC Exosome cells are much more potent and viable than our very own MSC and have the most growth factors during this time period which increases the end results.
What is Theradome Helmet?
The Theradome Helmet is a hair-stimulating laser device invented by a former NASA scientist, with a Ph.D. in Biomedical Engineering. He found that when combining cold lasers, red light therapy, optimal energy dose and maximum therapy you could regrow hair in the comfort of your own home. Lasers have a high energy density to stimulate hair follicles deep within the scalp, unlike light emitting diodes (LED) which are similar to a light bulb, laser light is “coherent” light meaning highly focused. The Theradome also uses cool laser phototherapy to regrow hair for best results which target stem cells at the base of the hair follicle. By treating the base of the hair follicles, the cold laser ensures that the mitochondria within the cell is activated. The mitochondria then produces cell energy that is harnessed by the hair follicles. It is important to penetrate the area of hair loss at the appropriate depth with subsequent energy absorption. Different wavelengths of light will result in distinct laser energies, which enter human tissue at various depths. However, hair follicles can only absorb coherent laser light at a wavelength of 680 ± 8 nanometers (nm). The Theradome harnesses the power of red light at an optimized wavelength of 680 nm, which is ideal for clinical strength hair growth therapy. It is also important that laser phototherapy treatments have the correct energy dosage otherwise the hair growth treatment will be ineffective. According to the Swedish Laser Medical Society, optimal energy density delivered to the scalp will trigger a cellular response of the hair follicle improving density and overall quality of hair while accelerating hair regrowth.
How to use the Helmet? I recommend my patients use it every other day for 20 minutes for the entire length of the treatment or when they are satisfied with their results, approximately 16-52 weeks. The studies have shown that during the first 16 weeks (4 months) hair loss will be minimized. The following 2-3 months is when the hair follicle becomes thicker and fuller, reversing miniaturization. The remainder of the year (5-6 months) is the final step of hair growth. Once you see the results you are trying to achieve, you can reduce your treatment from every other day to 2-3x a week. But just like going to the gym, you must continue to wear your theradome helmet to maintain your results.
What exactly is red light therapy? Red Light Therapy is an everyday term used to describe photobiomodulation. Photobiomodulation is defined as the utilization of non-ionizing electromagnetic energy to trigger photochemical changes within cellular structures that are receptive to photons. Mitochondria, the powerhouse of your cell and the organelle responsible for producing energy, is particularly receptive to this process. Meaning, at the cellular level, visible red and near-infrared light (NIR) energy is absorbed by the mitochondria which allows this powerhouse organelle to produce more energy in the form of ATP. The key to this entire process is a mitochondrial enzyme called cytochrome oxidase c which accepts the photonic energy of specific wavelengths when it is not functioning correctly. Biological reactions to light are nothing new, our bodies absorb (through our skin) and convert Vitamin D through a photochemical reaction via the sunlight. Our vision is no different. Our eyes, which are photosensitive, create a chemical reaction when the light hits our retinas allowing us to see. But near infrared light (NIR) doesn’t just activate the mitochondria, it also releases a byproduct of the mitochondrial metabolism known as mild oxidants (ROS) which in turn releases Nitric Oxide (NO). Nitric Oxide is a potent vasodilator which is responsible for increased blood flow and circulation. This improved blood flow, improved mitochondrial energy and the release of mild oxidants allows for cellular repair and healing.
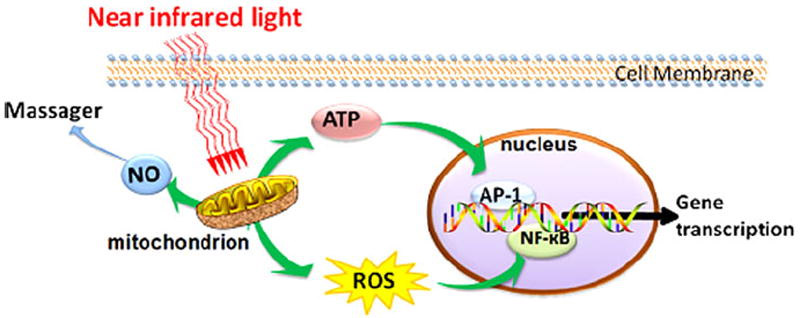
What is the History of Light Therapy? Red Light Therapy was first discovered by the ancient Egyptians who constructed solariums fitted with colored glass to harness specific colors of the visible spectrum from sunlight to heal disease. But it wasn’t until the early 1900’s that ultraviolet light was used in the treatment of Tuberculosis, winning a Nobel Prize in Medicine. Later on, incandescent light bulbs were used to treat diabetes, chronic fatigue, insomnia, baldness and other health issues. In the 1960’s, the first LASER (Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation) was invented and used to accelerate wound healing and coincidentally grew hair as a side effect. Red Light Therapy, as we know it, didn’t start to flourish until the 2000’s with now over 50,000 published clinical studies on the benefits of using Red Light Therapy as well as its safety profile. Red Light Therapy uses 600-700 nanometer wavelength radiation which can penetrate the skin by 8-10 mm which is enough to absorb the light and cause a diverse range of metabolic events to include: increased circulation and formation of new blood vessels, increased lymph system activity, increased production of collagen and fibroblasts, increased release of ATP (cellular energy), increased phagocytosis (the clean up of cellular debris), the stimulation of tissue granulation (the tissue formed during wound healing) and reduced inflammation. However, there is such a thing as too much or too little light with these treatments. If the wavelength is too low, then it will not be absorbed and without absorption there is no chemical reaction. If the wavelength is too high, then too much heat is emitted and in turn will burn the tissue creating inflammation and damage.
What is Nutrafol?
Nutrafol is a dietary product that is designed to nourish and strengthen thinning hair from within. It is formulated with botanical ingredients that are clinically proven. It features the latest technology that standardizes the ingredients to specifically target the multiple triggers of hair loss; hormones, inflammation and stress. Nutrafol also acts as a preventative and anti-aging regimen to maintain healthy hair growth and thickness. Initial results can be seen in 3-6 months with many patients seeing increased hair growth in as little as two months and reporting decreased shedding and improved thickness. As discussed before, the reason for hair loss in men and women are different. Men naturally produce more Testosterone and therefore convert into their active metabolite, dihydrotestosterone (DHT) which is also known as the stronger androgen. DHT is the hormone related to male pattern hair loss. Nutrafol for Men contains more of the natural DHT blocker, saw palmetto, than the women’s version. Whereas, the women’s version has higher levels of collagen and Vitamin C for inflammation and stress.
Nutrafol contains clinically tested, bio-optimized, botanical nutraceutical ingredients and help with hair loss by: balancing and lowering cortisol levels and other stress hormones, repairing and preventing inflammation and oxidative stress, rebalancing damaging hair hormones like DHT, improving circulation and blood flow as well as providing necessary nutritional building blocks for hair production.
The main function of each of the ingredients include:
1. Ashwagandha: stress adaptogen and reduces inflammation as well as free radicals and oxidative stress
2. Tocotrienols: a super antioxidant, reduces inflammation, free radicals and oxidative stress
3. Saw Palmetto: natural DHT-inhibitor and reduces inflammation
4. Curcumin: super anti-inflammatory as well as reduces DHT production, reduces stress hormones, reduces free radicals and oxidative stressSide Benefits:
Many Nutrafol users report significant and varied benefits beyond improved hair growth. Due to the stress adaptogenic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and anti aging properties of the ingredients, many Nutrafol users report experiencing decreased anxiety, improved sleep, decreased sugar cravings, and improved skin health.
Does not contain gluten, wheat, shellfish or binders
How to Take Nutrafol? 4 capsules a day with food, preferably in the morning as most patient’s report, improved energy and focus throughout the day. The studies have shown that taking Nutrafol for at least 4 months is required to see the full potential and benefits of hair growth.
What is a Peptide?
Peptides are made up of a string of amino acids. Amino acids are the building blocks for making proteins and peptides. There are 20 amino acids, and nine of them are considered essential amino acids since our bodies cannot produce them. These essential amino acids include histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine. This just means that we need to consume certain foods to obtain those specific essential amino acids such as meat, fish, poultry, eggs, milk, cheese, yogurt, and soybeans. Peptides are naturally occurring building blocks in the body and consist of 50 amino acid sequences or less. They are synthesized for signaling molecules and hormones in the body through your DNA, mimicking what your body naturally produces. Anything above 50 amino acids is considered to be a protein and is an essential part of all living organisms, especially as structural components of body tissues such as muscle, hair, collagen, enzymes, and antibodies. These proteins can become complicated structures whereas peptides are considered to be simplistic. All peptides are synthetic since large-scale proteins are hard to make and each amino acid is put together piece by piece to assimilate and mimic the complicated structure that makes up each individual peptide. Peptide therapy has been around for about 30 years in Australia and about 50 years in Russia. The actual science of peptides has been around since the 1970s and continues to grow. Insulin is the very first peptide of its kind for the treatment of diabetes. We have close to 300,000 peptides in our body and we are still learning about what they specifically do. For example, collagen peptides are isolated from natural products and come from bone marrow, fish, or marine animals. Collagen peptides promote the health of bones and joints and contribute to health and elasticity of the skin. Some peptides are used for the treatment of hormone regulation, weight loss, repair and recovery, cancer treatment, and telomere lengthening just to name a few. I use quite a bit of peptide therapy in my practice but there are specific peptides that I want to focus on for the treatment of hair loss and restoration.
Peptides we use in our Protocol include:
1. Hair Rescue: Repair, otherwise known as GHK-Cu and Zn-Thymulin
2. Hair Rescue: Activate, otherwise known as PTD-DBM with Methyl Vanillate
3. Thymosin Beta 4 or Fragment (Ac-SDKP)
How To Use Hair Rescue: Repair or GHK-Cu and Zinc Thymulin
Hair Rescue: Repair works by combining two potent peptide combinations, GHK-Cu and Zn-Thymulin. In studies, GHK-Cu has been shown to strengthen existing hair by stimulating growth in areas that are lacking in thickness. Zn-Thymulin is a combination of Zinc and a nonapeptide called Thymulin. Together, Zn-Thymulin has been shown to extend the anagen phase of hair follicles and reduce hair loss associated with a zinc deficiency.
GHK-Cu is a Copper tri-peptide that is naturally occurring and has a high affinity for copper. It is isolated from human plasma and found in saliva and urine. GHK-Cu has a variety of roles in the human body including promotion of wound healing, powerful anti-oxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, stimulating collagen synthesis in skin fibroblasts, promoting blood vessel growth and hair follicle stimulation. A decline in GHK coincides with noticeable decrease in rejuvenation capacity. GHK-Cu for the treatment of hair loss has been shown to increase hair follicle stimulation by stimulating proliferation of dermal fibroblasts. It also elevates production of VEGF which promotes hair growth and follicle size by improving vascularity around the hair follicle. It decreases inflammation and is superior to Minoxidil or Rogaine and has no rebound effect, meaning once you discontinue using it you will not shed the hair you regrew as you would with Minoxidil.
The other benefits to using GHK-Cu include: activates wound healing, including gastric wound healing, attracts immune cells, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory, stimulates collagen and glycosaminoglycan synthesis in skin fibroblasts, modulates the activity of both metalloproteinases and their inhibitors, angiogenic (formation of new blood vessels), improves cell systems, tumor defense, restores replicative vitality to fibroblasts after radiation therapy, skin regeneration.
Zinc Thymulin (Zn-Thymulin) is a combination of zinc and a nonapeptide called Thymulin. Thymulin is produced by two distinct epithelial populations in the thymus and first described by Back in 1977. Thymulin requires zinc for biological activity. The hormone is involved in T-cell differentiation and enhancement of T and NK cell actions. Thymulin has neuroendocrine effects as well. It follows a circadian rhythm and physiologically elevated ACTH levels correlate positively with thymulin plasma levels and vice versa. A recent study was done on Zinc Thymulin to test its efficacy in the treatment of hair loss. The study indicated that topical treatment with zinc thymulin significantly increased hair growth over 6 months; further, there were no systemic or local side effects from the treatment. The zinc thymulin metallo-peptide optionally also improves endogenous hair pigmentation. For example, by stimulating melanogenesis in grey or greying hair.
How to use the Hair Rescue: Repair? Apply 1mL (dropperful) on your scalp once daily at bedtime. Most studies show that using topically for more than 6 months has no adverse effect and maintains the hair follicle in its anagen stage.
How To Use Hair Rescue: Activate or PTD-DBM with Methyl Vanillate
Hair Rescue: Activate combines a potent hair-stimulating peptide, PTD-DBM with Methyl Vanillate to provide a multi-approach solution to hair loss. Research shows these ingredients work synergistically to activate Wnt/Beta-catenin pathways via inhibition of CXXC5. CXXC-type zinc finger protein 5 (CXXC5) is a negative regulator of the Wnt/ß-catenin pathway which has been associated with hair restoration and wound healing. Follicle development and formation can be impeded by CXXC5 binding with the protein Dishevelled. PTD-DBM is a very recently created peptide which interferes with the binding process of CXXC5 and Dishevelled. This particular pathway has been proven to help rescue DHT-induced hair follicle miniaturization associated with male pattern baldness. This formula has been shown to stimulate normal hair growth and promote hair cell proliferation- helping hair appear thicker and fuller in as little as five weeks.
Methyl Vanillate is a plant-derived chemical compound which has been shown to activate the Wnt/Beta-catenin signaling pathway, increasing hair count and hair mass index.
Main Benefits: Reduces DHT-induced hair follicle miniaturization, promotes hair cell proliferation, encourages normal hair follicle development. This peptide is often used as a part of larger hair protocols in conjunction with other peptides such as GHK-Cu, Zn-Thymulin, and Thymosin Beta with tremendous results.
How to use the Hair Resuce: Activate? Apply 1mL (dropperful) on your scalp once daily in the morning.
How To Use Thymosin Beta 4 or Ac-SDKP Fragment
The Thymus gland is responsible for fighting infection, reducing inflammation, and activating the immune system. Thymosin peptides are endogenous peptides that stimulate the development and differentiation of T lymphocytes. They play a role in regulating the immune system by stimulating other kinds of immune cells as well. Several factors control the release of these peptides, including the presence of foreign organisms, chemical messengers from white blood cells, levels of pituitary and other hormones (cortisol, estrogen, etc.) as well as nervous stimulation. The immune system undergoes age-associated alterations, which accumulate to produce a progressive deterioration in the ability to respond to infections and to develop immunity after vaccination or exposure, both of which are associated with a higher mortality rate in the elderly. Immunosenescence is defined as the specific changes in the immune system associated with age- related dysregulation and dysfunction of the immune system. Thymic involution, and hence output, is a decisive factor responsible for the inability to replace naïve T cells as they are “used up” by exposures over the life course. Thymic involution is a developmentally programmed event seen in most mammals, occurring around puberty, by which time the requirement to maximize immune defenses to reach reproductive age has been achieved and the resource-intensive and potentially dangerous process of generating large numbers of new T cells is no longer paramount. This in turn causes a Thymosin deficiency.
Thymosin Beta 4 is a protein that consists of 43 amino acids and is encoded by gene TMSBX4. It is present in all human cells, naturally found in higher concentrations in damaged tissue. It is the second hormone secreted by the Thymus gland and is responsible for decreasing injury time and reduced delayed onset of muscle soreness. Its primary function is to stimulate the production of T cells, which are an important part of the immune system. It also assists in the development of B cells to plasma cells to produce antibodies. It is the predominant form of Thymosin and is a member of a highly conserved family of actin monomer-sequestering proteins. It plays a role in tissue repair by protection, regeneration and remodeling of injured or damaged tissue. It has also been shown to regrow hair when added to PRP protocols as it influences the growth of blood vessels around the hair follicle and activates cell migration.
How to use Thymosin Beta 4? This peptide comes in an injectable form dosed at 0.25mL subQ daily, preferable in the morning as it may give you energy. Since this peptide causes angiogenesis, it is important to use 2 months on and 1 month off, allowing your body a “drug holiday”.
Ac-SDKP Fragment is a naturally occurring prolyl oligopeptidase tetrapeptide degradation product of Thymosin Beta-4, one of the most widely prescribed and well-studied peptides, which is naturally found in most cells. TB4 Frag, the active peptide in its precursor Thymosin Beta-4, is released as Thymosin Beta-4 is broken down. TB4 Frag has been found to have many health benefits such as pro-angiogenic, decreased fibrosis in the lungs and heart, anti-inflammatory, proliferation, and regeneration of new neurons. TB4 Frag has many mechanisms of action, some are still being researched currently.
How to use Ac-SDKP Fragment? Take one 5mg capsule by mouth daily, again due to its angiogenic properties a “drug holiday” is required after 2 months of taking.
Get the support you need.
Experience compassionate care and tailored solutions for your sexual health and anti-aging concerns. We will work with you to enhance satisfaction and wellbeing.

